Lidar Laser technology has rapidly become an essential tool across various industries, transforming the way we collect and analyze spatial data. According to Dr. Emily Hart, a leading expert in remote sensing and Lidar Laser applications, "The precision and versatility of Lidar Laser technology have unlocked new possibilities for mapping and understanding our environment." This statement encapsulates the incredible impact that Lidar Laser has had in fields ranging from agriculture to urban planning.
As we delve into the top 10 applications of Lidar Laser technology, it is important to recognize how it contributes to enhancing our decision-making processes and improving efficiency. By leveraging high-resolution data, professionals can achieve a level of accuracy and detail previously thought unattainable. From creating detailed topographical maps to supporting ecological conservation efforts, the potential uses for Lidar Laser technology continue to expand, showcasing its vital role in advancing innovation and sustainability across multiple sectors.
In an era where data-driven insights are paramount, embracing Lidar Laser technology is not just beneficial but necessary. The following sections will explore the most impactful applications of this cutting-edge technology, highlighting its significance and the future possibilities that lie ahead.

Lidar technology, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, utilizes laser light to measure distances and create high-resolution maps of physical environments. The core principle behind Lidar involves sending out pulses of laser light and recording the time it takes for these pulses to bounce back after hitting an object. By calculating the time of flight, Lidar can accurately determine the distance to the object. This technology relies on the speed of light, enabling precise measurements over various terrains and conditions.
The working principles of Lidar are rooted in the interaction between light and surfaces. As the laser beams strike different materials, they can reflect, scatter, or absorb the incoming light, allowing Lidar systems to gather valuable data on surface characteristics. The collected data generates a detailed point cloud, which can be processed to create two-dimensional maps or three-dimensional models. This technique is particularly useful in applications such as topographical mapping, forestry analysis, and urban planning, as it provides unique insights into spatial relationships and landscape features that traditional surveying methods may overlook.
Lidar laser technology is revolutionizing multiple industries by providing precise distance measurements and detailed environmental modeling. In the field of autonomous vehicles, Lidar is essential for navigation and obstacle detection, enabling safe travel through complex environments. By mapping surroundings in real-time, it allows self-driving cars to make quick decisions and respond to potential hazards effectively. Additionally, the technology plays a significant role in urban planning, where detailed topographical data helps city planners design infrastructure, manage resources, and implement smart city concepts.
Another key industry benefiting from Lidar is agriculture. This technology facilitates precision farming practices by mapping crop fields and optimizing resource distribution. Farmers can analyze data to improve yield, monitor plant health, and manage irrigation systems more efficiently. In environmental studies, Lidar is invaluable for forestry management, allowing researchers to assess tree density, biomass, and vegetation health.
It also aids in flood modeling and disaster management, providing critical data to anticipate and mitigate natural disasters impacting communities. These diverse applications highlight the transformative potential of Lidar laser technology across various sectors.
Lidar technology has emerged as a revolutionary tool in environmental monitoring, enabling researchers and policymakers to gain unprecedented insights into various ecosystems. One of its most prominent applications is forest management, where Lidar systems facilitate detailed mapping of forest structure. This allows for the assessment of tree density, height, and biomass, providing data essential for sustainable forestry practices and conservation efforts. By understanding the three-dimensional arrangement of trees, authorities can better manage resources and monitor changes over time due to factors like climate change and human activity.
Another significant application of Lidar in environmental monitoring is assessing coastal erosion and changes in land use. By employing Lidar to capture high-resolution elevation data of coastal areas, scientists can accurately track and model shoreline shifts and the impact of rising sea levels. This information is crucial for effective planning and implementing strategies to mitigate coastal hazards. Additionally, Lidar’s ability to penetrate vegetation makes it a valuable tool in wetland monitoring, providing insights into the health of these critical ecosystems and enhancing conservation strategies. Through these applications, Lidar plays a vital role in promoting environmental sustainability and informed decision-making in the face of ongoing ecological challenges.
Lidar technology has emerged as a pivotal component in the evolution of autonomous vehicles, offering unparalleled precision in environmental mapping and information gathering. By emitting rapid laser pulses and measuring the reflected light, lidar systems can create detailed three-dimensional maps of the surroundings, allowing vehicles to identify obstacles, road conditions, and potential hazards in real time. According to a report by the International Society of Automation, the global lidar market for automotive applications is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% from 2021 to 2026, highlighting its increasing importance in the automotive sector.
In autonomous driving, lidar serves as an essential tool for both perception and decision-making processes. Unlike traditional camera systems that may struggle in adverse weather conditions, lidar can function effectively in low-light situations or inclement weather, significantly enhancing vehicle safety. Additionally, a study conducted by the Transportation Research Board revealed that vehicles equipped with lidar can reduce the incidence of accidents by up to 40%, underscoring the technology’s potential to revolutionize road safety. As researchers continue to optimize lidar sensors for size and cost efficiency, the pursuit of fully autonomous vehicles appears more attainable than ever.
| Application | Description | Benefits | Impact on Autonomous Vehicles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obstacle Detection | Uses Lidar to identify and locate obstacles around the vehicle. | Improved safety and awareness of surroundings. | Enhances decision-making for navigation. |
| Real-Time Mapping | Creates accurate 3D maps of the environment. | Detailed spatial awareness for smarter routing. | Facilitates adaptive learning and navigation. |
| Traffic Monitoring | Analyzes traffic flow and road conditions. | Optimizes travel routes and reduces congestion. | Improves overall efficiency in route planning. |
| Night Vision Assistance | Provides visibility in low-light conditions using Lidar. | Increased safety during nighttime driving. | Enhances vehicle performance in various conditions. |
| Pedestrian Detection | Identifies and tracks the movement of pedestrians. | Increases safety for pedestrians and drivers. | Reduces the risk of accidents in urban areas. |
| Adaptive Cruise Control | Adjusts the vehicle's speed based on real-time traffic. | Enhances comfort and fuel efficiency. | Supports smoother traffic flow and reduced stress. |
| Road Condition Assessment | Monitors road surface conditions and hazards. | Supports proactive maintenance and repair. | Increases vehicle longevity and performance. |
| Lane Departure Warning | Alerts drivers when unintentionally leaving a lane. | Helps prevent accidents due to drifting. | Improves overall driving safety. |
| Environmental Modeling | Creates detailed models of the surrounding environment. | Supports autonomous systems in understanding their environment. | Facilitates improved interactions with complex environments. |
| Integration with Other Sensors | Combines data from Lidar with cameras and radar. | Enhances data accuracy and environmental understanding. | Supports robust autonomous navigation and decision-making. |
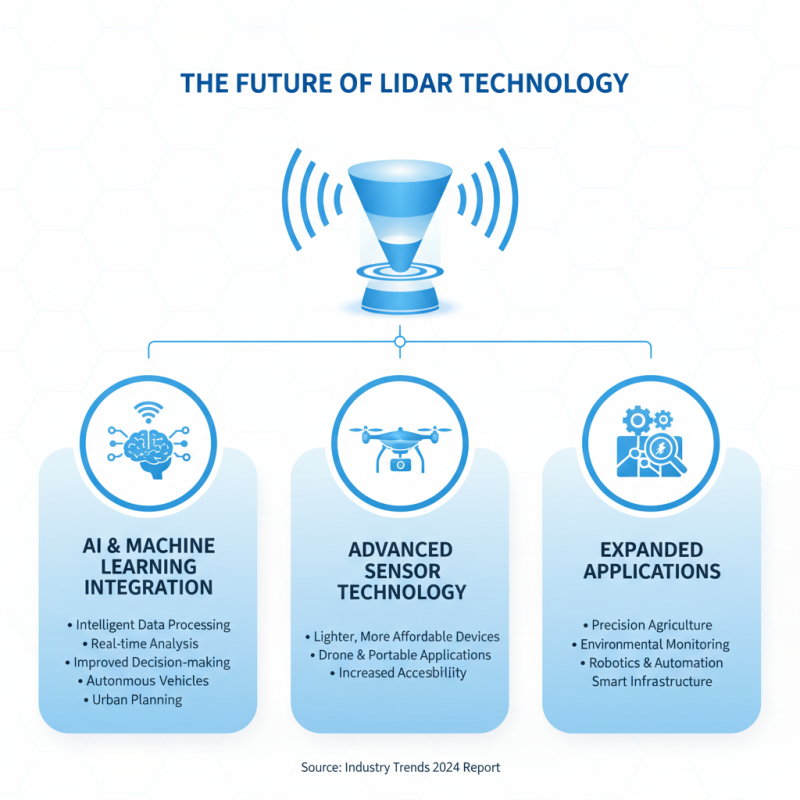
Lidar technology continues to evolve rapidly, shaping various industries with its precision and versatility. As we look towards the future, several trends are emerging that promise to enhance its applications further. One such trend is the integration of AI and machine learning with Lidar systems. This combination enables more intelligent data processing, allowing for real-time analysis and improved decision-making in sectors like autonomous vehicles and urban planning. Additionally, advancements in sensor technology are leading to lighter, more affordable Lidar devices that can be used in drones and portable applications, expanding accessibility for smaller businesses and individuals.
Tips: When considering the adoption of Lidar technology, it's essential to stay abreast of emerging software solutions that can seamlessly integrate with Lidar data. These tools can significantly enhance the analysis capabilities, making it easier to derive actionable insights. Furthermore, exploring partnerships with tech companies dedicated to innovation in Lidar can provide a competitive edge.
Another promising development is the refinement of multi-spectral Lidar, which captures additional information beyond distance measurements. This technology is particularly valuable in forestry management and agriculture, as it allows for the assessment of plant health and terrain characteristics in greater detail. As Lidar continues to gain traction, its potential applications will only become more diverse, driving growth across various fields.
Tips: For those looking to leverage multi-spectral Lidar, consider investing in training programs to better understand data interpretation. This knowledge can help you maximize the benefits of the rich data collected and inform strategic decisions for land and resource management.